14 KiB
| eip | title | author | discussions-to | status | type | category | created |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1822 | Universal Upgradeable Proxy Standard (UUPS) | Gabriel Barros <gabriel@terminal.co>, Patrick Gallagher <blockchainbuddha@gmail.com> | https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/eip-1822-universal-upgradeable-proxy-standard-uups | Stagnant | Standards Track | ERC | 2019-03-04 |
Table of contents
- Table of contents
- Simple Summary
- Abstract
- Motivation
- Terminology
- Specification
- Pitfalls when using a proxy
- Examples
- References
- Copyright
Simple Summary
Standard upgradeable proxy contract.
Abstract
The following describes a standard for proxy contracts which is universally compatible with all contracts, and does not create incompatibility between the proxy and business-logic contracts. This is achieved by utilizing a unique storage position in the proxy contract to store the Logic Contract's address. A compatibility check ensures successful upgrades. Upgrading can be performed unlimited times, or as determined by custom logic. In addition, a method for selecting from multiple constructors is provided, which does not inhibit the ability to verify bytecode.
Motivation
-
Improve upon existing proxy implementations to improve developer experience for deploying and maintaining Proxy and Logic Contracts.
-
Standardize and improve the methods for verifying the bytecode used by the Proxy Contract.
Terminology
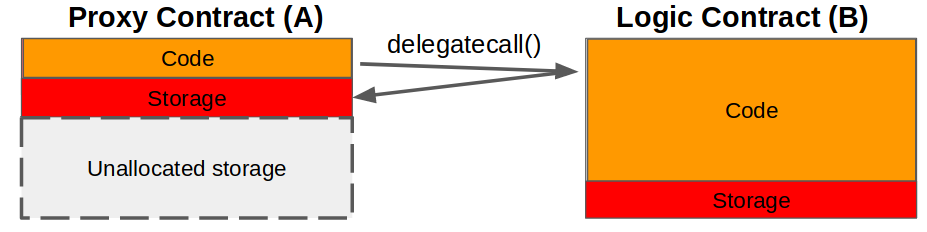
delegatecall()- Function in contract A which allows an external contract B (delegating) to modify A's storage (see diagram below, Solidity docs)- Proxy Contract - The contract A which stores data, but uses the logic of external contract B by way of
delegatecall(). - Logic Contract - The contract B which contains the logic used by Proxy Contract A
- Proxiable Contract - Inherited in Logic Contract B to provide the upgrade functionality
Specification
The Proxy Contract proposed here should be deployed as is, and used as a drop-in replacement for any existing methods of lifecycle management of contracts. In addition to the Proxy Contract, we propose the Proxiable Contract interface/base which establishes a pattern for the upgrade which does not interfere with existing business rules. The logic for allowing upgrades can be implemented as needed.
Proxy Contract
Functions
fallback
The proposed fallback function follows the common pattern seen in other Proxy Contract implementations such as Zeppelin or Gnosis.
However, rather than forcing use of a variable, the address of the Logic Contract is stored at the defined storage position keccak256("PROXIABLE"). This eliminates the possibility of collision between variables in the Proxy and Logic Contracts, thus providing "universal" compatibility with any Logic Contract.
function() external payable {
assembly { // solium-disable-line
let contractLogic := sload(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7)
calldatacopy(0x0, 0x0, calldatasize)
let success := delegatecall(sub(gas, 10000), contractLogic, 0x0, calldatasize, 0, 0)
let retSz := returndatasize
returndatacopy(0, 0, retSz)
switch success
case 0 {
revert(0, retSz)
}
default {
return(0, retSz)
}
}
}
constructor
The proposed constructor accepts any number of arguments of any type, and thus is compatible with any Logic Contract constructor function.
In addition, the arbitrary nature of the Proxy Contract's constructor provides the ability to select from one or more constructor functions available in the Logic Contract source code (e.g., constructor1, constructor2, ... etc. ). Note that if multiple constructors are included in the Logic Contract, a check should be included to prohibit calling a constructor again post-initialization.
It's worth noting that the added functionality of supporting multiple constructors does not inhibit verification of the Proxy Contract's bytecode, since the initialization tx call data (input) can be decoded by first using the Proxy Contract ABI, and then using the Logic Contract ABI.
The contract below shows the proposed implementation of the Proxy Contract.
contract Proxy {
// Code position in storage is keccak256("PROXIABLE") = "0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7"
constructor(bytes memory constructData, address contractLogic) public {
// save the code address
assembly { // solium-disable-line
sstore(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7, contractLogic)
}
(bool success, bytes memory _ ) = contractLogic.delegatecall(constructData); // solium-disable-line
require(success, "Construction failed");
}
function() external payable {
assembly { // solium-disable-line
let contractLogic := sload(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7)
calldatacopy(0x0, 0x0, calldatasize)
let success := delegatecall(sub(gas, 10000), contractLogic, 0x0, calldatasize, 0, 0)
let retSz := returndatasize
returndatacopy(0, 0, retSz)
switch success
case 0 {
revert(0, retSz)
}
default {
return(0, retSz)
}
}
}
}
Proxiable Contract
The Proxiable Contract is included in the Logic Contract, and provides the functions needed to perform an upgrade. The compatibility check proxiable prevents irreparable updates during an upgrade.
⚠️ Warning:
updateCodeAddressandproxiablemust be present in the Logic Contract. Failure to include these may prevent upgrades, and could allow the Proxy Contract to become entirely unusable. See below Restricting dangerous functions
Functions
proxiable
Compatibility check to ensure the new Logic Contract implements the Universal Upgradeable Proxy Standard. Note that in order to support future implementations, the bytes32 comparison could be changed e.g., keccak256("PROXIABLE-ERC1822-v1").
updateCodeAddress
Stores the Logic Contract's address at storage keccak256("PROXIABLE") in the Proxy Contract.
The contract below shows the proposed implementation of the Proxiable Contract.
contract Proxiable {
// Code position in storage is keccak256("PROXIABLE") = "0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7"
function updateCodeAddress(address newAddress) internal {
require(
bytes32(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7) == Proxiable(newAddress).proxiableUUID(),
"Not compatible"
);
assembly { // solium-disable-line
sstore(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7, newAddress)
}
}
function proxiableUUID() public pure returns (bytes32) {
return 0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7;
}
}
Pitfalls when using a proxy
The following common best practices should be employed for all Logic Contracts when using a proxy contract.
Separating Variables from Logic
Careful consideration should be made when designing a new Logic Contract to prevent incompatibility with the existing storage of the Proxy Contract after an upgrade. Specifically, the order in which variables are instantiated in the new contract should not be modified, and any new variables should be added after all existing variables from the previous Logic Contract
To facilitate this practice, we recommend utilizing a single "base" contract which holds all variables, and which is inherited in subsequent logic contract(s). This practice greatly reduces the chances of accidentally reordering variables or overwriting them in storage.
Restricting dangerous functions
The compatibility check in the Proxiable Contract is a safety mechanism to prevent upgrading to a Logic Contract which does not implement the Universal Upgradeable Proxy Standard. However, as occurred in the parity wallet hack, it is still possible to perform irreparable damage to the Logic Contract itself.
In order to prevent damage to the Logic Contract, we recommend restricting permissions for any potentially damaging functions to onlyOwner, and giving away ownership of the Logic Contract immediately upon deployment to a null address (e.g., address(1)). Potentially damaging functions include native functions such as SELFDESTRUCT, as well functions whose code may originate externally such as CALLCODE, and delegatecall(). In the ERC-20 Token example below, a LibraryLock contract is used to prevent destruction of the logic contract.
Examples
Owned
In this example, we show the standard ownership example, and restrict the updateCodeAddress to only the owner.
contract Owned is Proxiable {
// ensures no one can manipulate this contract once it is deployed
address public owner = address(1);
function constructor1() public{
// ensures this can be called only once per *proxy* contract deployed
require(owner == address(0));
owner = msg.sender;
}
function updateCode(address newCode) onlyOwner public {
updateCodeAddress(newCode);
}
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner, "Only owner is allowed to perform this action");
_;
}
}
ERC-20 Token
Proxy Contract
pragma solidity ^0.5.1;
contract Proxy {
// Code position in storage is keccak256("PROXIABLE") = "0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7"
constructor(bytes memory constructData, address contractLogic) public {
// save the code address
assembly { // solium-disable-line
sstore(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7, contractLogic)
}
(bool success, bytes memory _ ) = contractLogic.delegatecall(constructData); // solium-disable-line
require(success, "Construction failed");
}
function() external payable {
assembly { // solium-disable-line
let contractLogic := sload(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7)
calldatacopy(0x0, 0x0, calldatasize)
let success := delegatecall(sub(gas, 10000), contractLogic, 0x0, calldatasize, 0, 0)
let retSz := returndatasize
returndatacopy(0, 0, retSz)
switch success
case 0 {
revert(0, retSz)
}
default {
return(0, retSz)
}
}
}
}
Token Logic Contract
contract Proxiable {
// Code position in storage is keccak256("PROXIABLE") = "0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7"
function updateCodeAddress(address newAddress) internal {
require(
bytes32(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7) == Proxiable(newAddress).proxiableUUID(),
"Not compatible"
);
assembly { // solium-disable-line
sstore(0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7, newAddress)
}
}
function proxiableUUID() public pure returns (bytes32) {
return 0xc5f16f0fcc639fa48a6947836d9850f504798523bf8c9a3a87d5876cf622bcf7;
}
}
contract Owned {
address owner;
function setOwner(address _owner) internal {
owner = _owner;
}
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner, "Only owner is allowed to perform this action");
_;
}
}
contract LibraryLockDataLayout {
bool public initialized = false;
}
contract LibraryLock is LibraryLockDataLayout {
// Ensures no one can manipulate the Logic Contract once it is deployed.
// PARITY WALLET HACK PREVENTION
modifier delegatedOnly() {
require(initialized == true, "The library is locked. No direct 'call' is allowed");
_;
}
function initialize() internal {
initialized = true;
}
}
contract ERC20DataLayout is LibraryLockDataLayout {
uint256 public totalSupply;
mapping(address=>uint256) public tokens;
}
contract ERC20 {
// ...
function transfer(address to, uint256 amount) public {
require(tokens[msg.sender] >= amount, "Not enough funds for transfer");
tokens[to] += amount;
tokens[msg.sender] -= amount;
}
}
contract MyToken is ERC20DataLayout, ERC20, Owned, Proxiable, LibraryLock {
function constructor1(uint256 _initialSupply) public {
totalSupply = _initialSupply;
tokens[msg.sender] = _initialSupply;
initialize();
setOwner(msg.sender);
}
function updateCode(address newCode) public onlyOwner delegatedOnly {
updateCodeAddress(newCode);
}
function transfer(address to, uint256 amount) public delegatedOnly {
ERC20.transfer(to, amount);
}
}
References
Copyright
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.